below the recrystallisation temperature
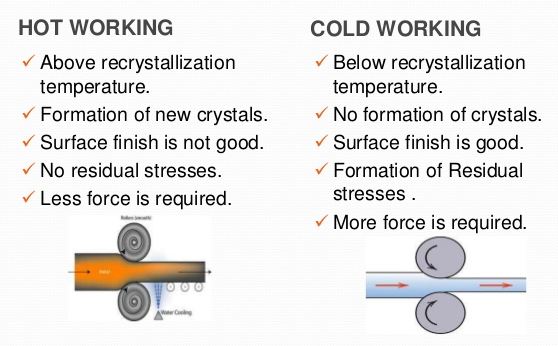
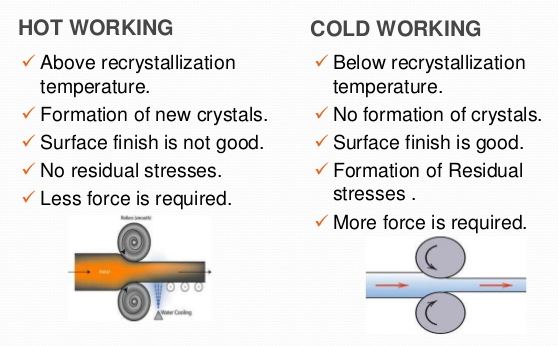
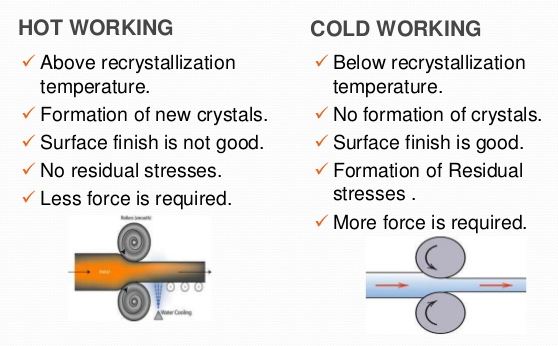
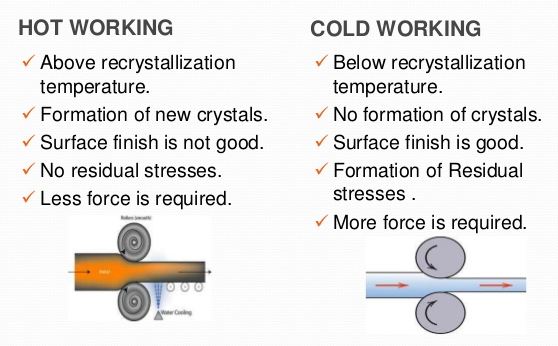
The working of metals below their recrystallisation temperature is known as cold working. Most of the cold working processes are performed at room temperature. The cold working distorts the grain structure and does not provide an appreciable reduction in size. It requires much higher pressure than hot working. The extent to which a metal can be cold worked depends upon its ductility. The higher the ductility of the metal, the more it can be cold worked. It also increases tensile strength , yield strength and hardness of steel but lowers its ductility. The increase in hardness due to cold working is called work-hardening.
The cold working of metals is carried out below the recrystallisation temperature.
work-hardening
Work hardening also called cold working is one of the process of increasing the strength of the material.
Work hardening is a very useful strengthening mechanism that occurs particularly in metallic materials through plastic deformation.
all of these
Work hardening is that which occurs in metalworking processes that intentionally induce plastic deformation to exact a shape change. These processes are known as cold working or cold forming processes. The cold working of the metal increases the hardness, yield strength, and tensile strength.
all of the above
Cold working is the plastic deformation of metals below the recrystallization temperature. In most cases, such cold forming is done at room temperature. The major cold-working operations can be classified basically as squeezing, bending, shearing and drawing.
is used for reducing the diameters of round bars and tubes by rotating dies which open and close rapidly on the work
Rotary swaging Is used for reducing the diameters of round bars and a tube by rotating dies which open and close rapidly on the work.