Compression ignition (C.I) engines
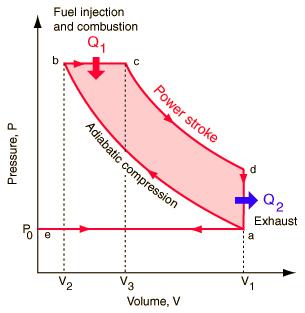
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to the mechanical compression. Hence diesel engines are also called as Compression ignition (C.I) engines.
Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
For the same maximum pressure and temperature Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle.
the heat of compression
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to the mechanical compression. Hence diesel engines are also called as Compression ignition (C.I) engines.
all of the above
Spark Ignition Engines
1. It works on Otto Cycle which is also called as constant volume cycle.
2. Fuel used is petrol.
3. During the suction stroke itself the petrol is first admitted in to the carburettor, where it gets mixed with the air and then mixture enters the cylinder.
4. Air and petrol mixture is drawn during the suction stroke.
5. Low compression ration ranging from 7:1 to 12:1.
6. The compressed air and petrol is ignited by the spark plug. This type of ignition is called spark ignition.
Spark Ignition Engines
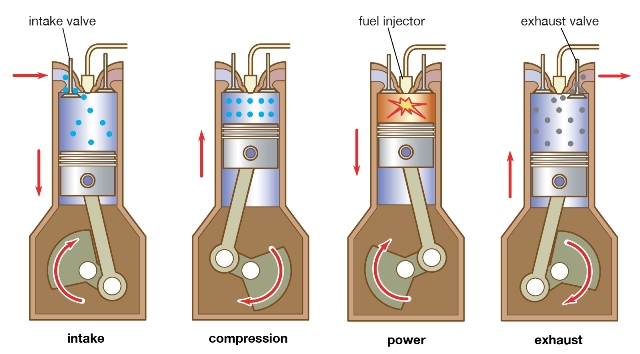
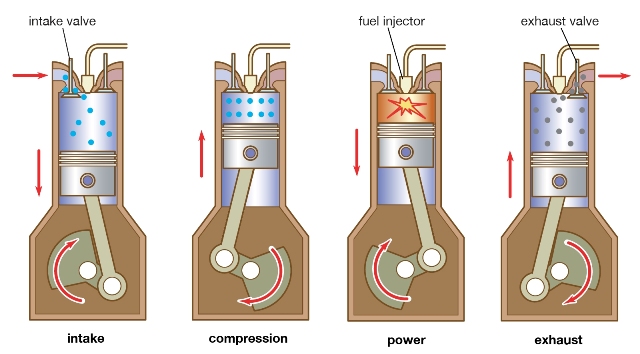
1. It works on Diesel Cycle which is also called as constant pressure cycle.
2. Fuel used is diesel.
3. The diesel oil is pressurised by the fuel pump and then injected into the engine cylinder by the fuel injector at the end of compression stroke.
4. Only air is drawn during the suction stroke.
5. High compression ratio ranging from 16:1 to 20:1.
6. The ignition of the diesel is accomplished by the compressed air which will have been heated due to high compression, to the temperature higher than the ignition temperature of the diesel. This type of ignition is called compression ignition or auto ignition.

constant pressure process
The combustion process in a Diesel engine is a constant pressure process.