Steel is an alloy of iron with greater than 0.02 % carbon but less than 2%, and cast iron is an alloy of iron containing a even more carbon between 2 and 4%.
Cast iron (usually, but not always) compared to steel has:
Higher damping ability.
Higher thermal capacity.
Higher fragility/ lower toughness.
Higher castability.
Higher stability at higher temperatures.
Lower cost.
Lower machinability.
Lower electric conductivity.
Lower thermal conductivity.
Lower plasticity.
Lower coefficient of friction.
Lower density.
3) In comparison to cast iron, steel is
more ductile and less harder
Related KPSC ITI JTO Fitter Question Papers - 2018 with Answer Key
above upper critical temperature line and cooled outside the furnace
Normalizing involves heating steel to above 50°C above the upper critical temperature, (for hypo-eutectoid steel) and to 50°C above the lower critical temperature (for hyper eutectoid steel). Holding at this temperature for a shorter time to prevent grain growth and finally, cooling in air.
slowest cooling rate that converts 100% austenite to 100% martensite
Critical Cooling Rate - The minimum rate of continuous cooling just sufficient to prevent undesired transformations. For steel, the slowest rate at which it can be cooled form above the upper critical temperature to prevent the decomposition of austenite at any temperature above the Ms. The limiting rate at which austenite must be cooled to ensure that a particular type of transformation product is formed.
Critical cooling rate is slowest cooling rate that converts 100% austenite to 100% martensite
37% lead and 63% tin
Electricians solder consists of 37% lead and 63% tin.
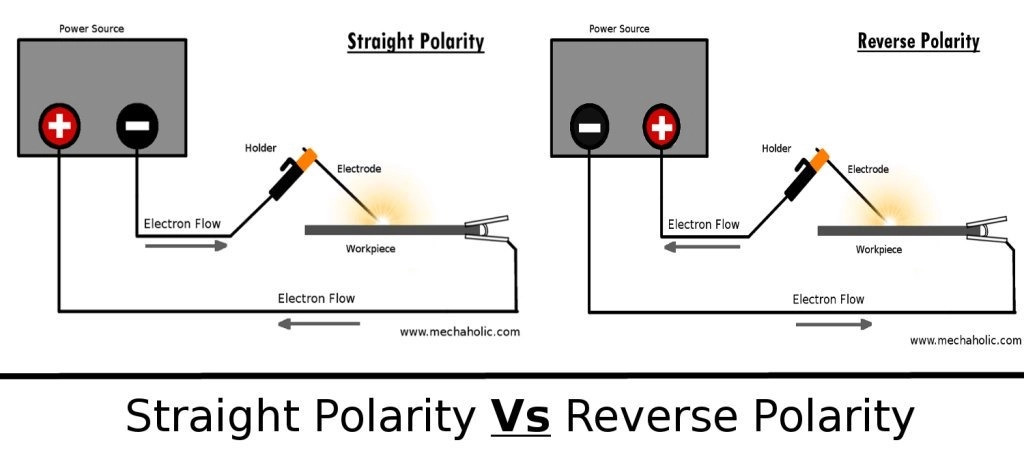
straight polarity is used
Direct Current Straight Polarity (DCSP) or Direct Current Electrode Negative (DCEN)—When electrode is connected with the negative terminal of the power source and base metals are connected with the positive terminal.
Metals with high melting temperature (such as stainless steel, titanium) can be suitably joined by DCSP.
Direct Current Reverse Polarity (DCRP) or Direct Current Electrode Positive (DCEP)—When base metals are connected with the negative terminal of the power source and electrode is connected with the positive terminal.
Metals with low melting temperature (such as copper, aluminum) can be suitably joined by DCSP.