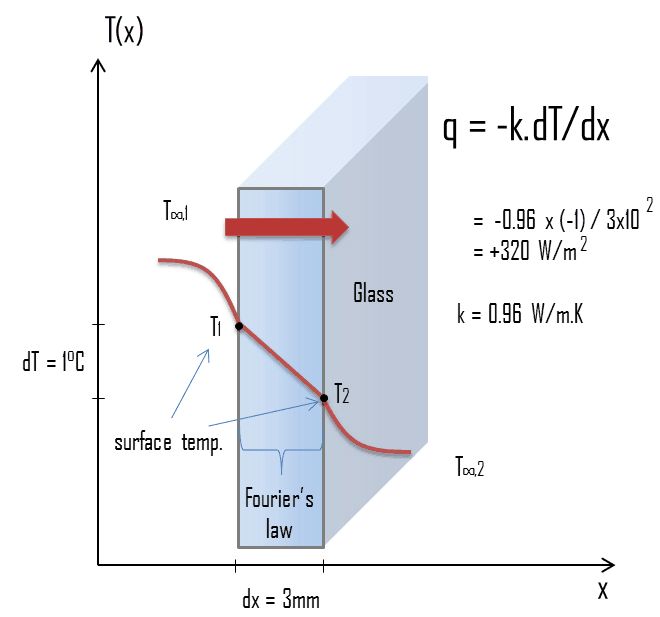
Otto cycle
Otto cycle is also known as constant volume cycle, as the heat is received and rejected at a constant volume. Otto cycle is used in gas, petrol and many of the oil engines. The petrol engine works on Otto cycle.
The ideal Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two reversible adiabatic or isentropic processes.
Otto cycle is taken as a standard of comparison for internal combustion engines. For the purpose of comparison with other cycles, the air is assumed to be the working substance.
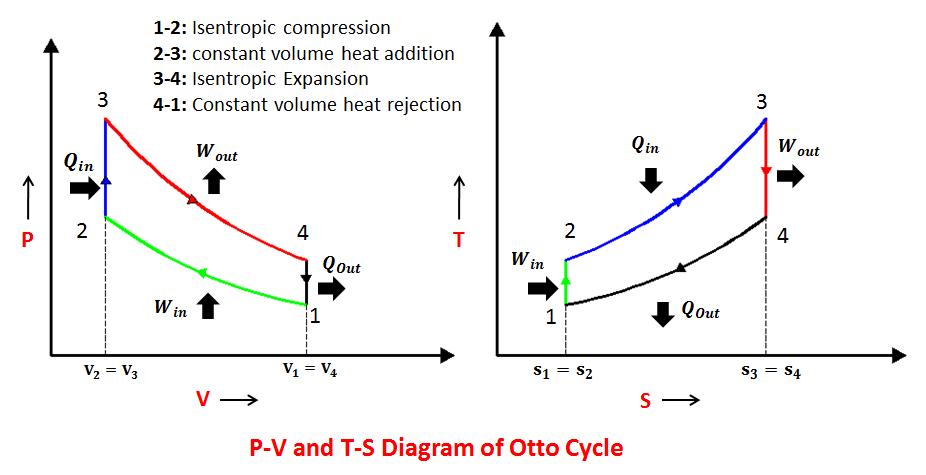
150 kPa (g)
The pressure increase from the free surface can be calculated with the formula for the weight of the water column divided by the cross sectional area, that is d*g*h, where
d = 1 000 kg/m^3 is water density,
g = 9.8 m/s^2 is gravity and
h = 15 m is the depth.
Then we get 147000 Pa = 147 kPa = 1.47 bar.
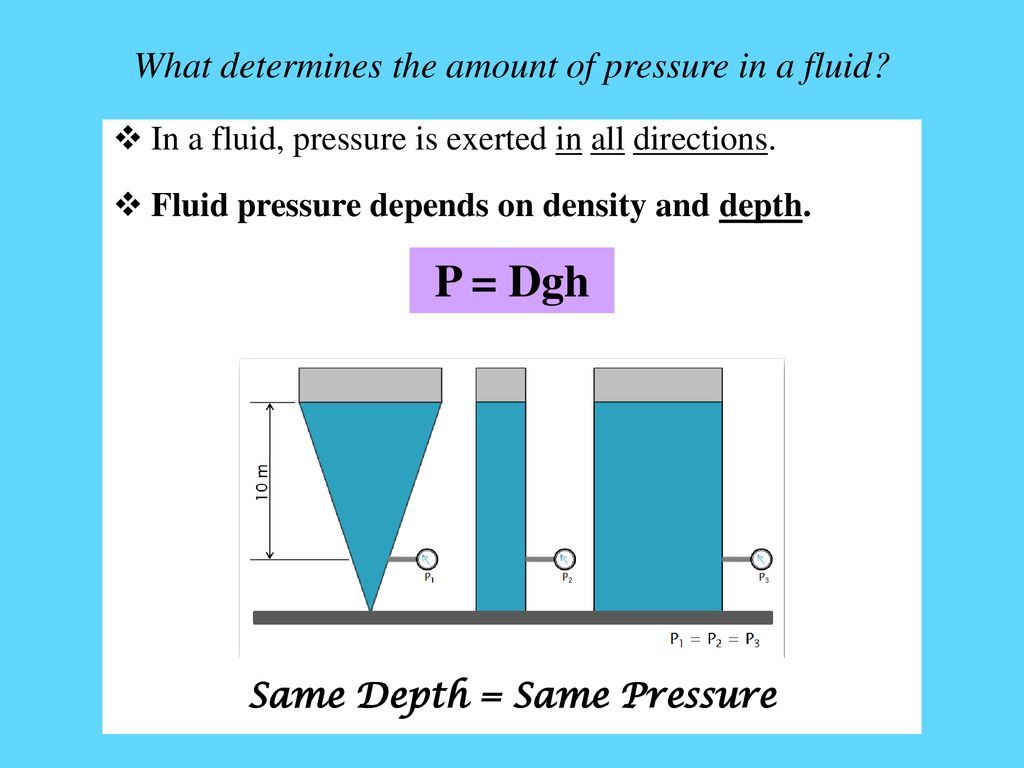
elongation
Ductility is the property of a material which enables it to draw out into thin wires.
The percent elongation and the reduction in area in tension is often used as empirical measures of ductility.
Ductility of material is indicated by elongation.
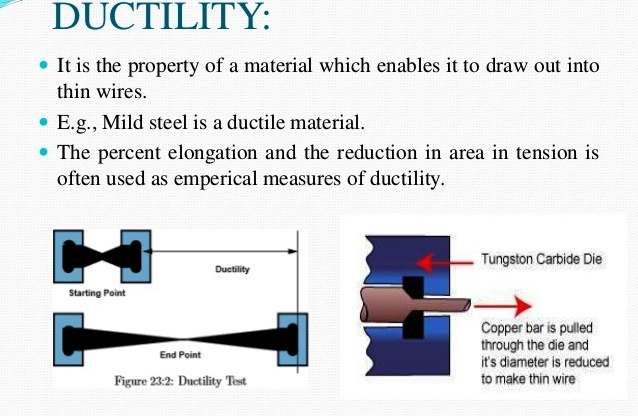
W/mK
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k.
Unit of thermal conductivity is W/mK.