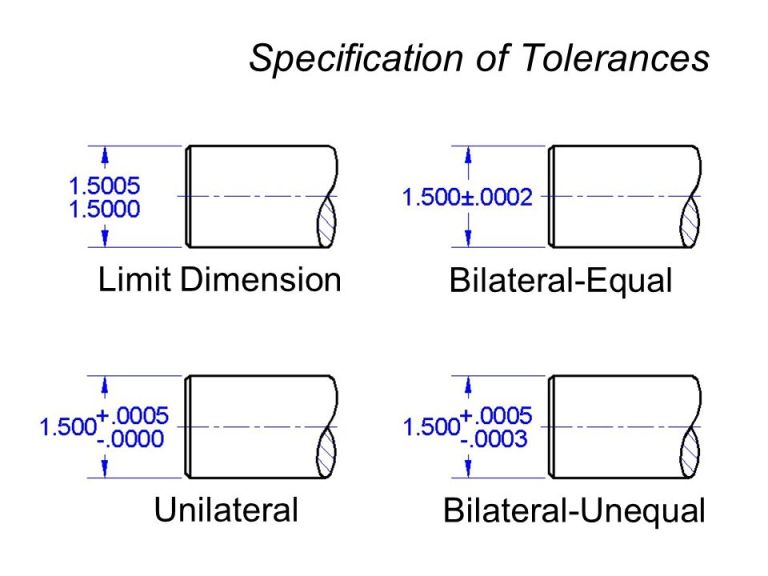
Bilateral tolerance is fixed on both sides of the basic size.
In unilateral tolerance, dimensions of a part is allowed to vary only on one side of basic size, either below or above the basic size.
One example may be given here as 1.5000 +0.0005 /-0.0000. Here the tolerance is 0.0005.
It can be comparable to bi-lateral tolerance method of specifying tolerance. An example for above may be 1.5000+0.0002/-0.0002 mm. Here the tolerance is 0.0004.
In the first case (Unilateral Tolerance), dimension is varying between 1.5005 and 1.5000 whereas in the second case (Bi-lateral Tolerance) dimension is varying between 1.4998 to 1.5002.
Application of unilateral system :
Unilateral system is preferred, especially when precision fits are required , because it is easy and simpler to determine deviations. Further, GO gauge ends can be standardized as the holes of different tolerance grades have the same lower limit and all the shafts have same upper limit.
Further, in unilateral system, this form of tolerance greatly assists the operator, when machining of mating parts. The operator maintain lower limit of holes, knowing fully well that he still has some margin left for machining before the part is is rejected.
Application of bilateral system:
In this system, the dimension of the part is allowed to vary on both sides of basic size , i.e. the limits of tolerance lie on either side of basic size, but may be necessarily equally disposed off.
10) Bilateral tolerance is fixed
On both sides ( upper and lower) of the basic size
Related Limits and Fits MCQ - Machinist(Set-1) with Answers
Ball Bearing on the shaft
Driving Fit - When a plug or a shaft is made slightly larger than the hole into which it is to be inserted and the allowance is such that the parts can be assembled by driving, this is known as driving fit.
Ball bearing on the shaft is the best example for driving fit.

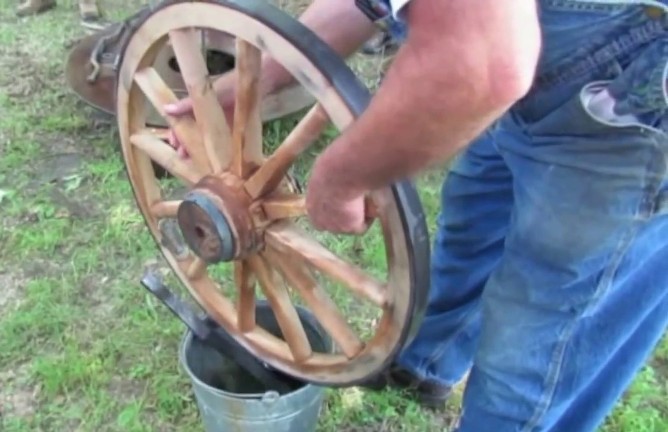
Cart rim on the wooden wheel
Best example for shrinkage fit is Cart rim on the wooden wheel.
Shrinkage fit A shrinkage fit is obtained by making the shaft (internal member) slightly larger than the hole (external member). In shrinkage fit, pressure is not required for assembling but instead the hole (external member) is heated and expanded sufficiently to permit the shaft (internal member) to be inserted easily. Then the hole (external member) is cooled to shrink tightly around the shaft (internal member).

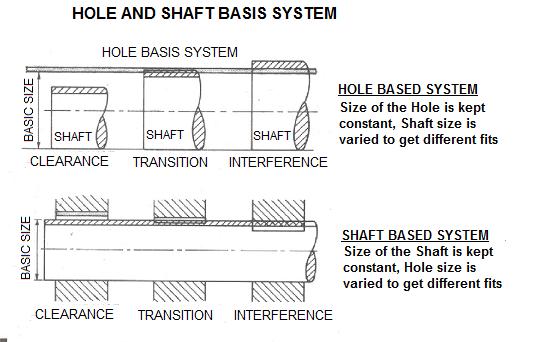
The size of the hole is made constant
In Hole basic system the size of the hole is made constant, different fits is obtained by varying shaft size.
Produce the parts within the required permissible size error
It is impossible to make anything to an exact size, therefore, it is essential to allow a definite tolerance or permissible variation on every specified dimension. Hence Tolerance is given to the part size to produce the parts, within the required permissible size error.