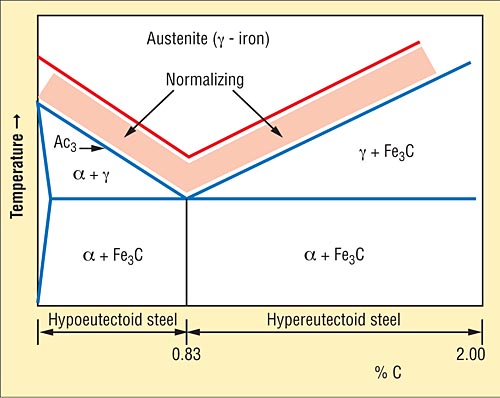
Normalizing Process involves heating a material to an elevated temperature and then allowing it to cool back to room temperature by exposing it to room temperature air after it is heated. This heating and slow cooling alters the microstructure of the metal which in turn reduces its hardness and increases its ductility
32) While normalizing the steel should be cooled
In still air to room temperature
Related Heat Treatment MCQ with Answers
Carburizing
Carburizing, also referred to as Case Hardening, is a heat treatment process that produces a surface which is resistant to wear, while maintaining toughness and strength of the core. This treatment is applied to low carbon steel parts after machining, as well as high alloy steel bearings, gears, and other components.
Case Hardening
Parts to be hardened by case hardening process are made from a steel with a carbon content of 0.15% so that they will not respond to direct hardening.
The steel is subjected to treatment in which the carbon content of the surface layer is increased to about 0.9%.
When the carburised steel is heated and quenched, only the surface layer will respond, and the core will remain soft and tough as required.
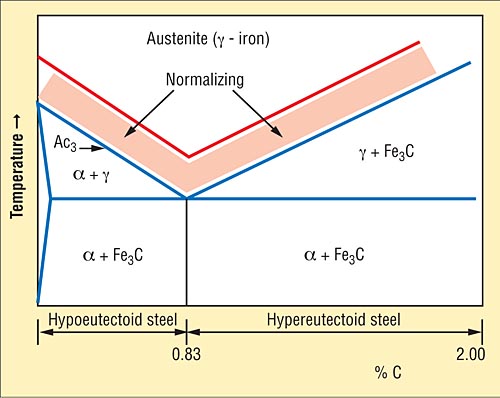
Normalizing
Normalizing involves heating a material to an elevated temperature and then allowing it to cool back to room temperature by exposing it to room temperature air after it is heated. This heating and slow cooling alters the microstructure of the metal which in turn reduces its hardness and increases its ductility.
Induction hardening
Induction hardening is a process used for the surface hardening of steel and other alloy components. The parts to be heat treated are placed inside a water cooled copper coil and then heated above their transformation temperature by applying an alternating current to the coil.