30) Which is an application layer of internet standard protocol used by local e-mail clients to retrieve e-mail from a remote server over a TCP/IP connection?
POP
Related Networking Concepts and Internet Concepts MCQ with Answers
Transport layer
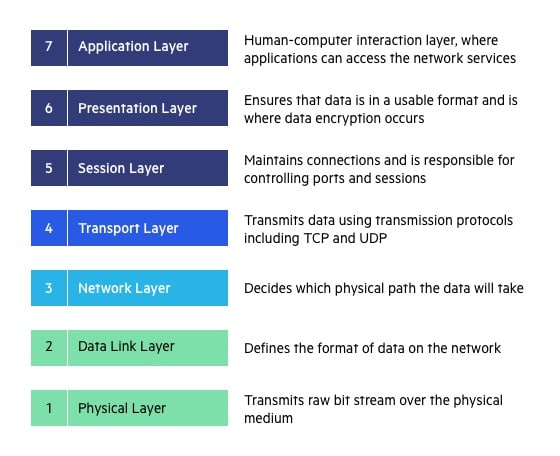
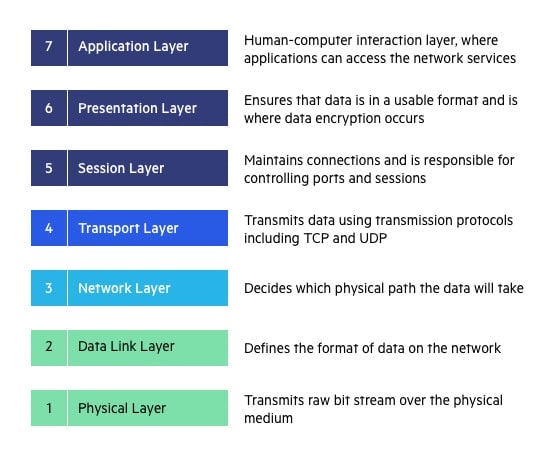
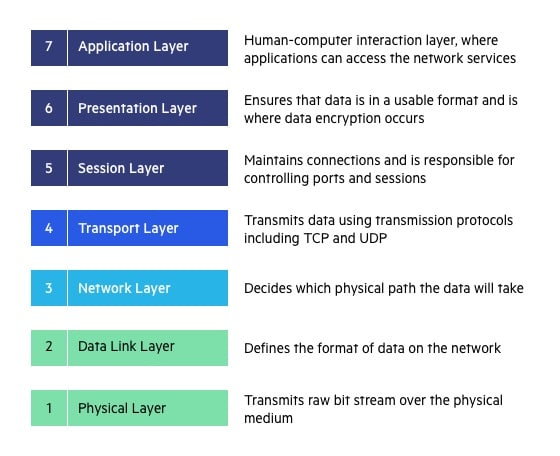
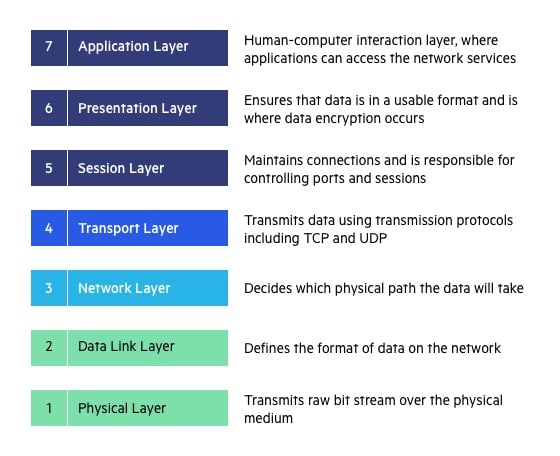
Transport Layer (Layer 4) :
The transport layer provides services to the application layer and takes services from the network layer. The data in the transport layer is referred to as Segments. It is responsible for the End to End Delivery of the complete message. The transport layer also provides the acknowledgement of the successful data transmission and re-transmits the data if an error is found.
• At sender’s side:
Transport layer receives the formatted data from the upper layers, performs Segmentation, and also implements Flow & Error control to ensure proper data transmission. It also adds Source and Destination port numbers in its header and forwards the segmented data to the Network Layer.
Note: The sender needs to know the port number associated with the receiver’s application.
Generally, this destination port number is configured, either by default or manually. For example, when a web application makes a request to a web server, it typically uses port number 80, because this is the default port assigned to web applications. Many applications have default ports assigned.
• At receiver’s side:
Transport Layer reads the port number from its header and forwards the Data which it has received to the respective application. It also performs sequencing and reassembling of the segmented data.
The functions of the transport layer are :
- Segmentation and Reassembly: This layer accepts the message from the (session) layer, breaks the message into smaller units. Each of the segments produced has a header associated with it. The transport layer at the destination station reassembles the message.
- Service Point Addressing: In order to deliver the message to the correct process, the transport layer header includes a type of address called service point address or port address. Thus by specifying this address, the transport layer makes sure that the message is delivered to the correct process.
The services provided by the transport layer :
- Connection-Oriented Service: It is a three-phase process that includes
– Connection Establishment
– Data Transfer
– Termination / disconnection
In this type of transmission, the receiving device sends an acknowledgement, back to the source after a packet or group of packets is received. This type of transmission is reliable and secure. - Connectionless service: It is a one-phase process and includes Data Transfer. In this type of transmission, the receiver does not acknowledge receipt of a packet. This approach allows for much faster communication between devices. Connection-oriented service is more reliable than connectionless Service.
passing traffic through the network to an end system
Layer 3
Network Layer (Layer 3) :
The network layer works for the transmission of data from one host to the other located in different networks. It also takes care of packet routing i.e. selection of the shortest path to transmit the packet, from the number of routes available. The sender & receiver’s IP addresses are placed in the header by the network layer.
The functions of the Network layer are :
- Routing: The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination. This function of the network layer is known as routing.
- Logical Addressing: In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, the network layer defines an addressing scheme. The sender & receiver’s IP addresses are placed in the header by the network layer. Such an address distinguishes each device uniquely and universally.
Layer 1
Physical Layer (Layer 1) :
The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next. When receiving data, this layer will get the signal received and convert it into 0s and 1s and send them to the Data Link layer, which will put the frame back together.
The functions of the physical layer are :
- Bit synchronization: The physical layer provides the synchronization of the bits by providing a clock. This clock controls both sender and receiver thus providing synchronization at bit level.
- Bit rate control: The Physical layer also defines the transmission rate i.e. the number of bits sent per second.
- Physical topologies: Physical layer specifies the way in which the different, devices/nodes are arranged in a network i.e. bus, star, or mesh topology.
- Transmission mode: Physical layer also defines the way in which the data flows between the two connected devices. The various transmission modes possible are Simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex.