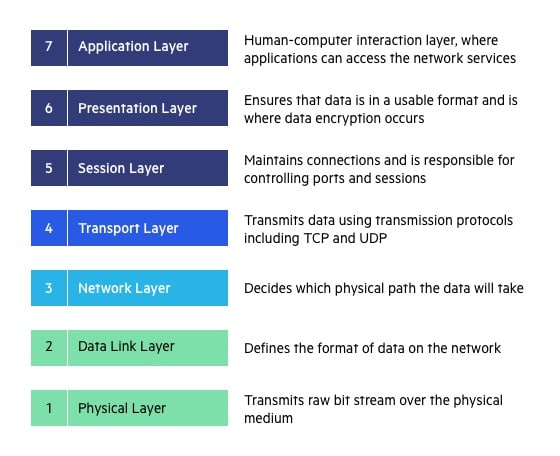
32) What is the purpose of the last three layers in OSI model?
passing traffic through the network to an end system
Related Networking Concepts and Internet Concepts MCQ with Answers
Layer 3
Network Layer (Layer 3) :
The network layer works for the transmission of data from one host to the other located in different networks. It also takes care of packet routing i.e. selection of the shortest path to transmit the packet, from the number of routes available. The sender & receiver’s IP addresses are placed in the header by the network layer.
The functions of the Network layer are :
- Routing: The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination. This function of the network layer is known as routing.
- Logical Addressing: In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, the network layer defines an addressing scheme. The sender & receiver’s IP addresses are placed in the header by the network layer. Such an address distinguishes each device uniquely and universally.
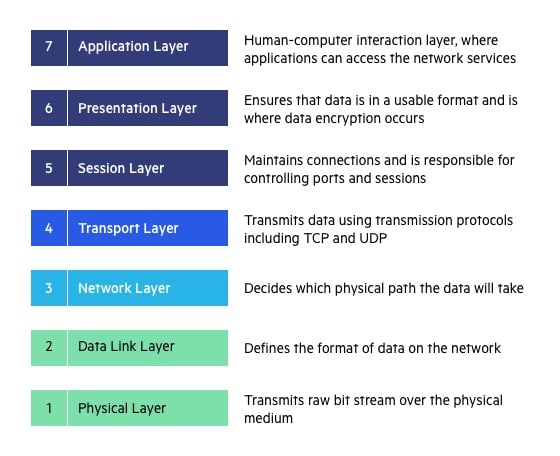
Layer 1
Physical Layer (Layer 1) :
The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next. When receiving data, this layer will get the signal received and convert it into 0s and 1s and send them to the Data Link layer, which will put the frame back together.
The functions of the physical layer are :
- Bit synchronization: The physical layer provides the synchronization of the bits by providing a clock. This clock controls both sender and receiver thus providing synchronization at bit level.
- Bit rate control: The Physical layer also defines the transmission rate i.e. the number of bits sent per second.
- Physical topologies: Physical layer specifies the way in which the different, devices/nodes are arranged in a network i.e. bus, star, or mesh topology.
- Transmission mode: Physical layer also defines the way in which the data flows between the two connected devices. The various transmission modes possible are Simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex.