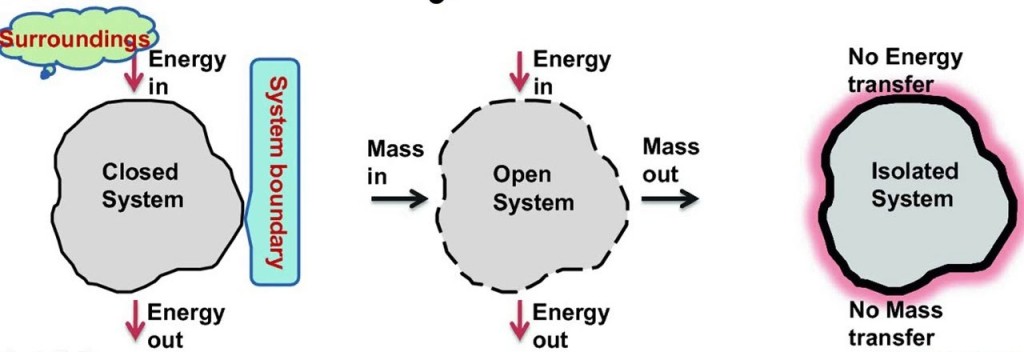
Classification of thermodynamic systems are
1. Closed system: Closed system is one in which boundary of the system does not allow the matter (mass) to cross it, then it is known as closed system. Here the system contains fixed or constant amount of matter (mass). Energy can cross the boundary. Heat and work are the only ways in which energy can be transferred between a closed system and its surroundings. Refrigerator is an example of Closed system.
2. Open system: Open system is one in which boundary of the system allows the matter (mass) to flow into or out of the system, then it is known as open system. In open system matter (Mass) crosses the boundary of the system. Heat and work may also cross the boundary.
3. Isolated system: Isolated system is one in which boundary of the system does not allow the matter (mass) or the energy to flow into or out of the system, then it is known as isolated system. An isolated system in one which is completely uninfluenced by the surroundings. It is of fixed mass and no heat or work crosses the boundary of the system.
78) Refrigerator is an example of
Answer is:
Closed system
Explanation:
Related Thermal Engineering MCQ with Answers
Answer is:
Two constant volume and two reversible adiabatic process
Explanation:
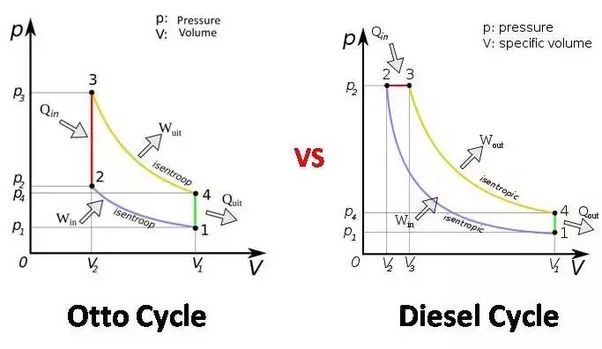
Diesel cycle is called constant pressure cycle because the heat addition process in diesel cycle is done at constant pressure whereas petrol cycle is called constant volume cycle (Otto Cycle) as here the heat addition is done at constant volume. (Heat rejection in both the cycles is done at constant volume).
Constant volume cycle involves Two constant volume and two reversible adiabatic process.