The formation of frost on cooling coils in a refrigerator increases power consumption.
6) The formation of frost on cooling coils in a refrigerator
increases power consumption

Related Heat Transfer Refrigeration and Air Conditioning MCQ with Answers
increases with increase in velocity of air passing through it
Bypass Factor is part of the total air through the coil which fails to come into contact with the surface of the cooling coil.
By-Pass factor is the inability of a coil to cool or heat the air to its temperature is indicated by a factor called by-pass factor (BPF) or Coil Bypass Factor. This inability is due to the coil inefficiency and some amount of air just bypassing the coil without getting affected by it.
The By-pass factor for a cooling coil increases with increase in velocity of air passing through it.
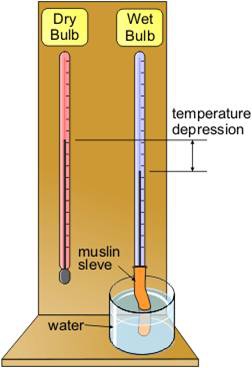
wet bulb depression
The wet-bulb depression is the difference between the dry-bulb temperature and the wet-bulb temperature. If there is 100% humidity, dry-bulb and wet-bulb temperatures are identical, making the wet-bulb depression equal to zero in such conditions.
The difference between dry bulb temperature and wet bulb temperature, is called wet bulb depression.
Correct
Defrosting or Thawing is the process of periodic melting of condensed water vapor on the cooling elements in the refrigerator cabinet.
Defrosting of a refrigerator may be done by stopping the compressor for a short period. Due to opening of the refrigerator door, outside air that contains water vapor enters the refrigerator cabinet. The water vapor in the air condenses on the cooling element ( evaporator coils) in the refrigerator. The accumulation of the condensed water on the evaporator coils lowers the cooling efficiency of the refrigerator. It becomes necessary to defrost the refrigerator in order to optimize it's cooling efficiency.

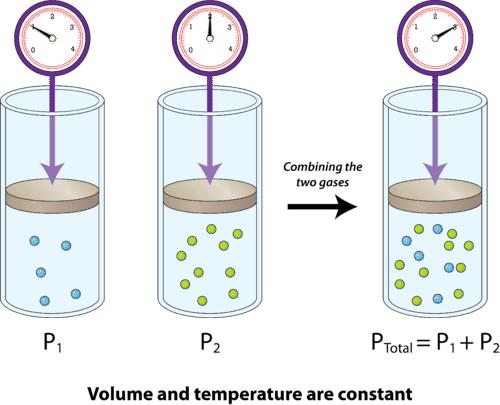
Pb = pa + pv
According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each of the constituent gases. The partial pressure is defined as the pressure each gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture at the same temperature.