Strength:
When external forces are applied on a metal, breaking (brittle metal) or yielding (ductile metal) may occur. Strength is the property of a metal by which it resists external force without breaking or yielding.
Stiffness:
When an external force is applied on a metal, it develops an internal resistance. The internal resistance developed per unit area is called stress. Stiffness is the ability of a metal to resist deformation under stress.
Toughness:
When a huge external force is applied on a metal, the metal will experience fracture. Toughness is the ability of a metal to resist fracture.
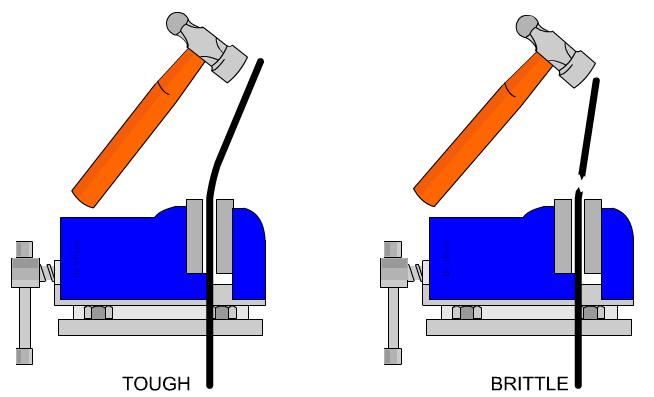
Brittleness
Brittleness is a property of material which breaks with little or no deformation.
7) which of the following property is desirable in parts subjected to shock and impact loads?
Toughness
Related Engineering Materials MCQ with Answers
Resilience
The strain energy stored in a body due to external loading within the elastic limit is known as resilience.
The property of a material essential for spring material is Resilience.
1. The maximum strain energy which can be stored in a body upto the elastic limit is called proof resilience.
2. The proof resilience per unit volume of a material is known as modulus of resilience.
decreases
Toughness: When a huge external force is applied on a metal, the metal will experience fracture. Toughness is the ability of a metal to resist fracture.
The toughness of material decreases when it is heated.
Mild steel
Ductility: Ductility is the property by which a metal can be drawn into thin wires. It is determined by percentage elongation and percentage reduction in area of a metal.
Mild Steel has maximum ductility.

Brittleness
Brittleness
Brittleness is a property of material which breaks with little or no deformation.
Plasticity:
Plasticity is the property by which a metal retains its deformation permanently, when the external force applied on it is removed.
Examples: forming, forging, hammering
Ductility:
Ductility is the property by which a metal can be drawn into thin wires. It is determined by percentage elongation and percentage reduction in area of a metal.
Malleability:
Malleability is the property by which a metal can be rolled into thin sheets. Highly malleable metals (like Mild Steel) are extensively used in making sheet metals.