Toughness: When a huge external force is applied on a metal, the metal will experience fracture. Toughness is the ability of a metal to resist fracture.
The toughness of material decreases when it is heated.
9) The toughness of material ______ when it is heated
decreases
Related Engineering Materials MCQ with Answers
Mild steel
Ductility: Ductility is the property by which a metal can be drawn into thin wires. It is determined by percentage elongation and percentage reduction in area of a metal.
Mild Steel has maximum ductility.

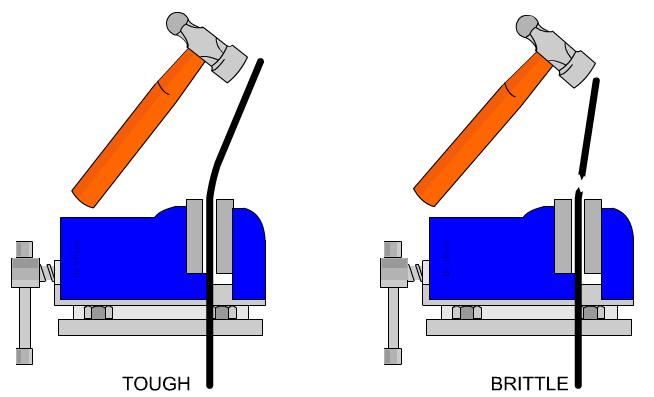
Brittleness
Brittleness
Brittleness is a property of material which breaks with little or no deformation.
Plasticity:
Plasticity is the property by which a metal retains its deformation permanently, when the external force applied on it is removed.
Examples: forming, forging, hammering
Ductility:
Ductility is the property by which a metal can be drawn into thin wires. It is determined by percentage elongation and percentage reduction in area of a metal.
Malleability:
Malleability is the property by which a metal can be rolled into thin sheets. Highly malleable metals (like Mild Steel) are extensively used in making sheet metals.
can cut another metal
Hardness is a very important property of the metals and has a wide variety of meanings. It embraces many different properties such as resistance to wear, scratching, deformation and machinability etc. It also means the ability of the metal to cut another metal.
The hardness is usually expressed in numbers which are dependent on the method of making the test.
Lead
Malleability:
Malleability is the property by which a metal can be rolled into thin sheets. Highly malleable metals (like Mild Steel) are extensively used in making sheet metals.
Lead is a soft, malleable, ductile, bluish-white, dense metallic element, extracted chiefly from galena and found in ore with zinc, silver and copper. Whilst it is still used for its malleability and corrosion resistance, it is its chemical properties that make it a thoroughly modern metal.
