Quantitative governing In this system of governing, the quality of charge (i.e. air-fuel ratio of the mixture) is kept constant. But the quantity of mixture supplied to the engine cylinder is varied by means of a throttle valve which is regulated by the centrifugal governor through rack and pinion arrangement.
The spark ignition engines are governed by Quantitative governing
the part load efficiency of SI engine is poor because air fuel ratio remains constant even if we need low power
Qualitative governing In this system of governing, a control valve is fitted in the fuel delivery pipe, which controls the quantity of fuel to be mixed in the charge. The movement of control valve is regulated by the centrifugal governor through rack and pinion arrangement.
The compression ignition engines are governed by Qualitative governing
part load efficiency of ci engine is good because we can use lean mixture and rich mixtures easily according to our requirement
3) The spark ignition engines are governed by
Quantative governing
Related KPCL AE Mechanical Question Paper - 2018 with Answer Key
Does not depend on the mass of the system, like temperature, pressure, etc.
Extensive properties The properties of the system, whose value for the entire system is equal to the sum of their values for the individual parts of the system, are called extensive properties.
For example, total volume, total mass and total energy of a system are extensive properties.
Intensive properties The properties of the system, whose value for the entire system is not equal to the sum of their values for the individual parts of the system, are called intensive properties.
For example, temperature, pressure and density of a system are intensive properties.
3mr2/10
4flv2/2gd
In fluid dynamics, the Darcy–Weisbach equation is an empirical equation, which relates the head loss, or pressure loss, due to friction along a given length of pipe to the average velocity of the fluid flow for an incompressible fluid. The equation is named after Henry Darcy and Julius Weisbach.

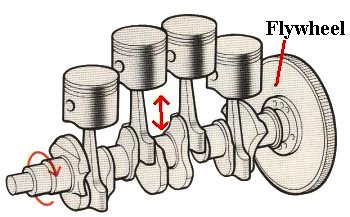
Flywheel
Flywheel. Flywheel, heavy wheel attached to a rotating shaft so as to smooth out delivery of power from a motor to a machine. The inertia of the flywheel opposes and moderates fluctuations in the speed of the engine and stores the excess energy for intermittent use.