In fusion welding process, penetration is the ratio of width of weld to the depth.
2) In fusion welding process, penetration is the ratio of
Width of weld to the depth
Related ISRO Technician-B Welder Question Paper - 2017 (Set -1) with Answer Key
Ultraviolet(UV)
Welding arcs give off radiation over a broad range of wavelengths - from 200 nm (nanometres) to 1,400 nm (or 0.2 to 1.4 µm, micrometres). These ranges include ultraviolet (UV) radiation (200 to 400 nm), visible light (400 to 700 nm), and infrared (IR) radiation (700 to 1,400 nm).
UV-radiation is divided into three ranges - UV-A (315 to 400 nm), UV-B (280 to 315 nm) and UV-C (100 to 280 nm). UV-C and almost all UV-B are absorbed in the cornea of the eye. UV-A passes through cornea and is absorbed in the lens of the eye.
Some UV radiation, visible light, and IR radiation can reach the retina.
Certain types of UV radiation can produce an injury to the surface and mucous membrane (conjunctiva) of the eye called "arc eye," "welders' eye" or "arc flash." These names are common names for "conjunctivitis" - an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the front of the eye.
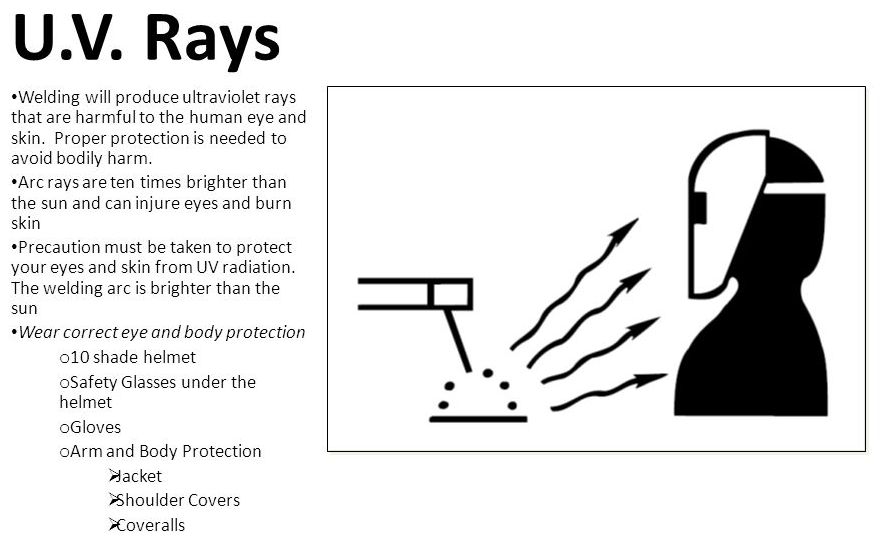
Leg length
The distance between the root and toe of a fillet weld is called leg length.
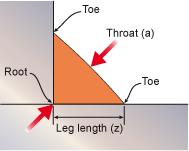
Fusion welding with pressure
Forge welding is a solid-state welding process that joins two pieces of metal by heating them to a high temperature and then hammering them together. It may also consist of heating and forcing the metals together with presses or other means, creating enough pressure to cause plastic deformation at the weld surfaces.
1.4 - 1.5
Coated Electrodes
Coated electrodes are classified according to the coating factor. Coating factor is the ratio of the diameter of the electrode to the diameter of the core wire.
So, following are sub types of coated electrodes:
Light coated electrodes with coating factor of 1.25. Light coating applied to electrodes helps to remove impurities such as oxides and phosphorous. Light coating also helps in enhancing arc stability.
Medium coated electrodes with coating factor of 1.45.
Heavily coated electrodes with coating factor ranging between 1.6 to 2.2. These electrodes have a proper and well defined composition. The heavily coated electrodes are designed in three types – electrodes with cellulose coating, electrodes with mineral coating and the electrodes with coating of both cellulose as well as mineral coating.
