6) What is the use of modem?
Connecting to internet
Data communication, IP addressing TCP/IP, Network Protocols MCQ with Answers
For more MCQ's Click HereRelated Data communication, IP addressing TCP/IP, Network Protocols MCQ with Answers
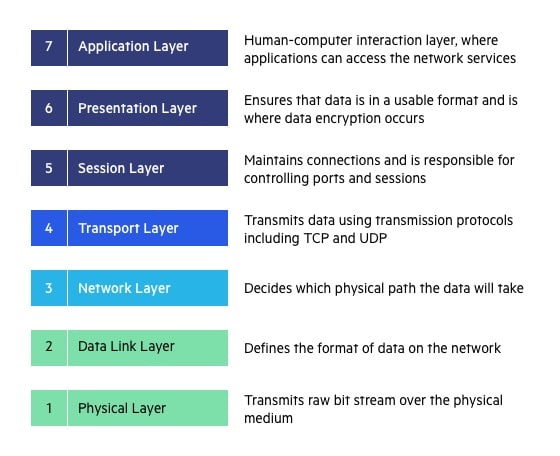
Layer 1
Physical Layer (Layer 1) :
The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next. When receiving data, this layer will get the signal received and convert it into 0s and 1s and send them to the Data Link layer, which will put the frame back together.
The functions of the physical layer are :
- Bit synchronization: The physical layer provides the synchronization of the bits by providing a clock. This clock controls both sender and receiver thus providing synchronization at bit level.
- Bit rate control: The Physical layer also defines the transmission rate i.e. the number of bits sent per second.
- Physical topologies: Physical layer specifies the way in which the different, devices/nodes are arranged in a network i.e. bus, star, or mesh topology.
- Transmission mode: Physical layer also defines the way in which the data flows between the two connected devices. The various transmission modes possible are Simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex.
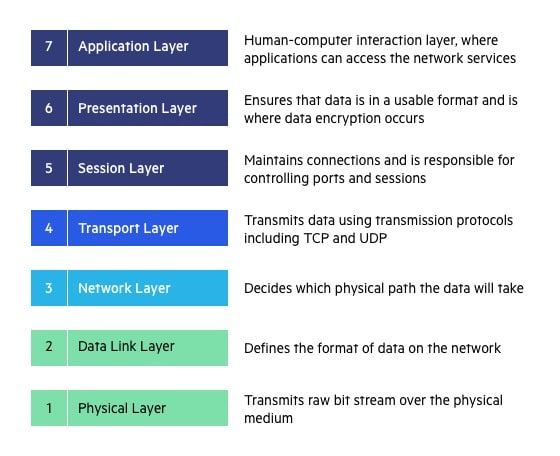
Layer 2
Data Link Layer (DLL) (Layer 2) :
The data link layer is responsible for the node-to-node delivery of the message. The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error-free from one node to another, over the physical layer. When a packet arrives in a network, it is the responsibility of DLL to transmit it to the Host using its MAC address.
Data Link Layer is divided into two sublayers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
- Media Access Control (MAC)
The packet received from the Network layer is further divided into frames depending on the frame size of NIC(Network Interface Card). DLL also encapsulates Sender and Receiver’s MAC address in the header.
The Receiver’s MAC address is obtained by placing an ARP(Address Resolution Protocol) request onto the wire asking “Who has that IP address?” and the destination host will reply with its MAC address.
The functions of the Data Link layer are :
- Framing: Framing is a function of the data link layer. It provides a way for a sender to transmit a set of bits that are meaningful to the receiver. This can be accomplished by attaching special bit patterns to the beginning and end of the frame.
- Physical addressing: After creating frames, the Data link layer adds physical addresses (MAC address) of the sender and/or receiver in the header of each frame.
- Error control: Data link layer provides the mechanism of error control in which it detects and retransmits damaged or lost frames.
- Flow Control: The data rate must be constant on both sides else the data may get corrupted thus, flow control coordinates the amount of data that can be sent before receiving acknowledgement.
- Access control: When a single communication channel is shared by multiple devices, the MAC sub-layer of the data link layer helps to determine which device has control over the channel at a given time.