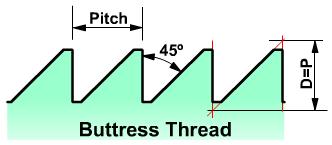
Buttress
Buttress thread form is designed to handle extremely high axial thrust in one direction. The load-bearing thread face is perpendicular to the screw axis. or at a slight slant (usually no greater than 7°). The other face is slanted, often at 45°
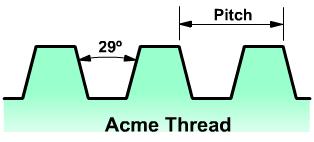
Acme
This thread is a modification of the square thread. It has an included angle of 29°. It is preferred for many jobs because it is fairly easy to machine.
Acme threads are used in lathe lead screws. This form of thread enables the easy engagement of the half nut. The metric acme thread has an included angle of 30°.
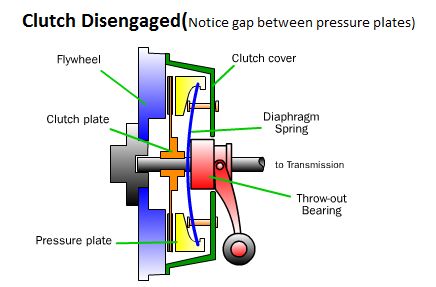
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device which engages and disengages power transmission especially from driving shaft to driven shaft.
In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member) while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. While typically the motions involved are rotary, linear clutches are also possible.
Clutch is used to bring the driven shaft to speed in gradual manner.
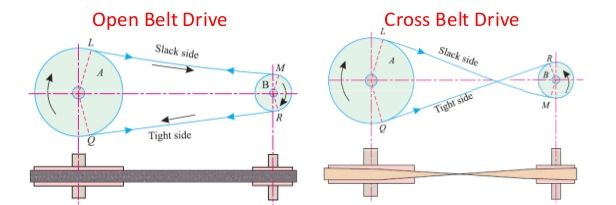
open belt drive
An open belt drive is used to rotate the driven pulley in the same direction of driving pulley. In the motion of belt drive, power transmission results make one side of pulley more tightened compared to the other side.
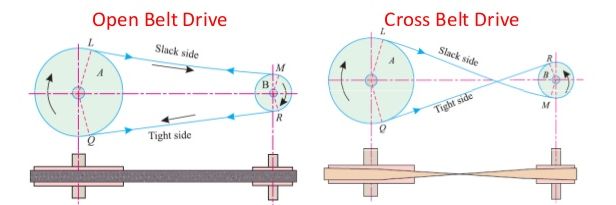
power transmission is less than open belt drive
Cross belt drive having parallel shafts rotating in opposite directions.
It is similar to open belt drive but the difference between these two belt drives are in crossed belt drive the direction of rotation is opposite to each other.
Here the pulleys are set up to offset position. By providing some misalignment between two pulleys.
Keep in mind one of the most important thing for Cross-belt drive application: It can be used anywhere where the high speed power transmission is required.