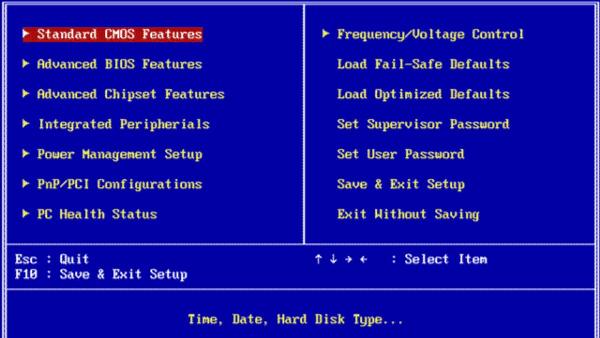
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) software interface does not directly interact with the operating system (OS). Rather, it provides a low-level interface between the major hardware components of the computer and the OS.
When a computer is powered on, the BIOS performs a series of checks and tests on the hardware to ensure that it's functioning properly. This is known as the Power-On Self-Test (POST), and it checks components such as the memory, hard drive, and CPU to make sure they're working correctly.
Once the POST is complete, the BIOS initializes the hardware components and provides the OS with the necessary information about the system hardware. This includes details about the motherboard, CPU, memory, hard drive, and other components.