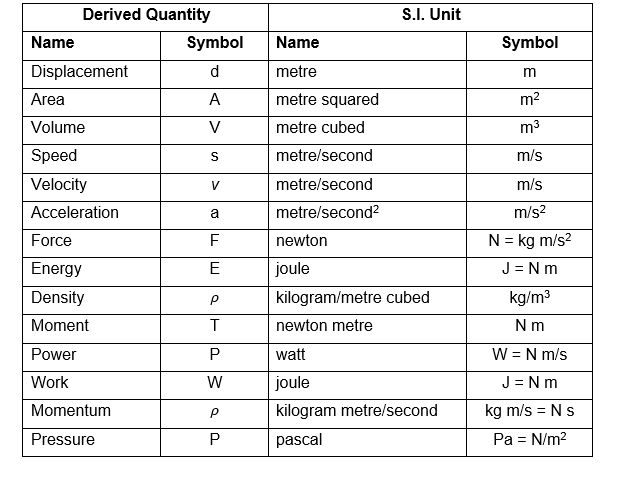
When a liquid is contained in a vessel, it exerts force at all points on the sides and bottom of the vessel. The force per unit area is called intensity of pressure. Mathematically, intensity of pressure,
p = P/A
where
P = Force acting on the liquid, and
A = Area on which the force acts.
The intensity of pressure may be expressed either in N/m2, N/mm2 or in metres of liquid or mm of liquid. Intensity of pressure is also expressed in pascal (briefly written as Pa), such that
1 Pa= 1 N/m2; 1 kPa= 1 kN/m2 and 1 MPa = 1 MN/m2= 1 N/mm2
11) The unit of pressure in S.I. units is
pascal
Related Engineering Thermodynamics MCQ with Answers
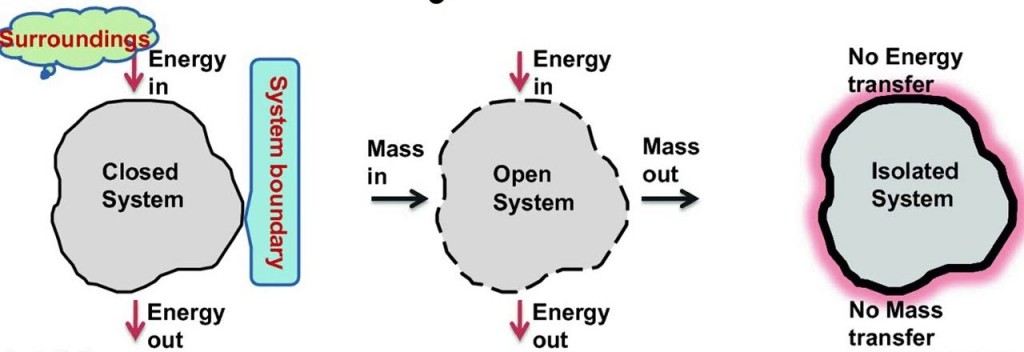
mass does not cross boundaries of the system, though energy may do so
Classification of thermodynamic systems are
1. Closed system: Closed system is one in which boundary of the system does not allow the matter (mass) to cross it, then it is known as closed system. Here the system contains fixed or constant amount of matter (mass). Energy can cross the boundary. Heat and work are the only ways in which energy can be transferred between a closed system and its surroundings.
2. Open system: Open system is one in which boundary of the system allows the matter (mass) to flow into or out of the system, then it is known as open system. In open system matter (Mass) crosses the boundary of the system. Heat and work may also cross the boundary.
3. Isolated system: Isolated system is one in which boundary of the system does not allow the matter (mass) or the energy to flow into or out of the system, then it is known as isolated system. An isolated system in one which is completely uninfluenced by the surroundings. It is of fixed mass and no heat or work crosses the boundary of the system.
kinetic energy of the molecules is zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvins.
At zero kelvin (minus 273 degrees Celsius) the particles stop moving and all disorder disappears. Thus, nothing can be colder than absolute zero on the Kelvin scale.
According to kinetic theory of gases, the absolute zero temperature is attained when kinetic energy of the molecules is zero.