Creep is defined as a time-dependent material deformation under continuous stress below the material’s yield strength. It is commonly observed to be quite impactful under elevated temperatures, especially with metals. Yet, it can still take place at room temperature, like with glass and lead, at a much slower rate.
Other names for creep include material creep and cold flow.
When materials are subjected to increasingly high-stress levels over a long period, creep can become severe. This especially applies to materials that are frequently exposed to high heat and can even permanently deform as temperatures reach the melting point. Without exceeding the material’s yield strength, creep can result in plastic strain, which is a unique aspect of this phenomenon, as plastic deformation generally happens when the yield strength is exceeded.
41) In the tensile test, the phenomenon of slow extension of the material, i.e. stress increasing with the time at a constant load is called
Answer is:
creeping
Explanation:
Related Engineering Materials MCQ with Answers
Answer is:
breaking stress
Answer is:
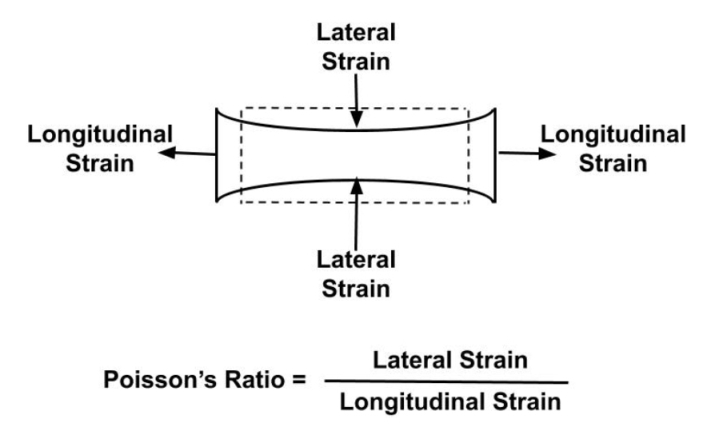
Poisson's ratio
Explanation:
Poisson's ratio is defined as the ratio of Lateral strain and longitudinal strain.