Adiabatic process or Isentropic process:
A process, in which the work substance neither receives nor gives out heat to its surroundings, during its expansion or compression is called an adiabatic process. This will happen when the working substance remains thermally insulated, so that no heat enters or leaves it during the process. It is thus obvious, that in an adiabatic process no heat leaves or enters the gas, the temperature of the gas changes, as the work is done at the cost of internal energy and the change in internal energy is equal to the work done.
An adiabatic process is one in which
* No heat enters or leaves the gas
* The temperature of the gas changes
* The change in internal energy is equal to the mechanical work done
6) An adiabatic process is one in which
all of the above
Related Thermodynamics MCQ with Answers
Incorrect
Water gas, colorless poisonous gas that burns with an intensely hot, bluish (nearly colorless) flame. The gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen with very small amounts of other gases, e.g. , carbon dioxide, and is almost entirely combustible as a result. Water gas is so named because of the use of water (steam) in its preparation. This process involves treating white-hot hard coal or coke with a blast of steam; carbon monoxide and hydrogen are formed. The gas is manufactured in vast quantities for commercial use. It is of much importance in the preparation of hydrogen and as a fuel in the making of steel and in other industrial processes.
Right
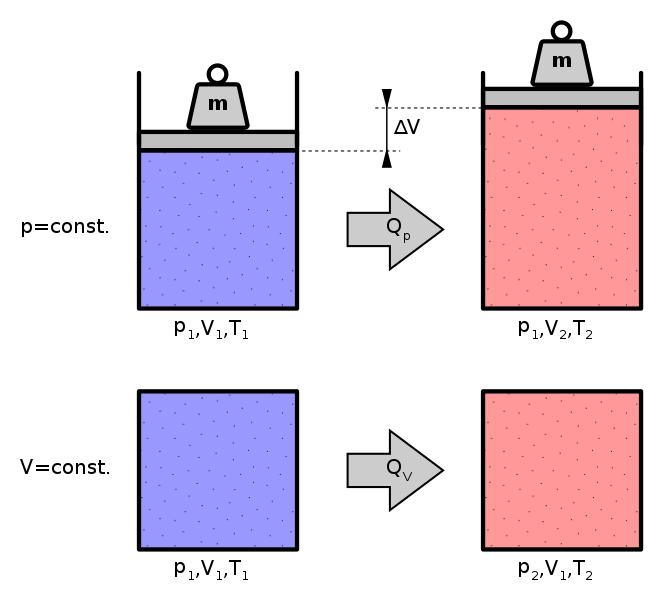
When the gas is heated at constant volume, the heat supplied increases the internal energy of the gas.
Gasoline
Gasoline or petrol is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines. Gasoline is the lightest and most volatile liquid fuel.

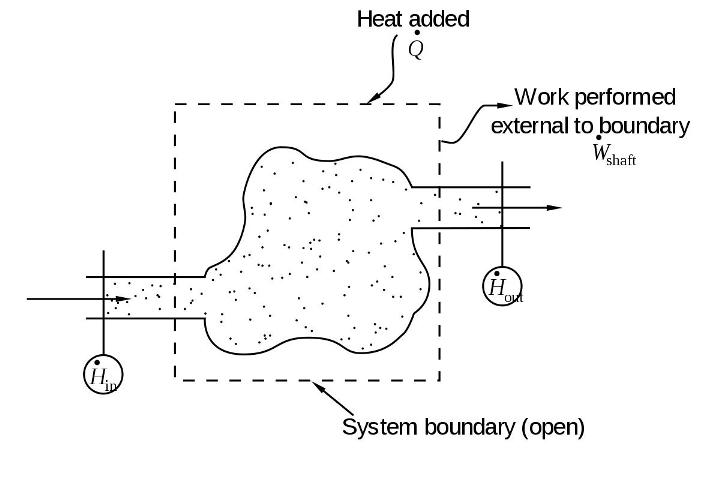
flow processes
Flow processes is one in which fluid enters the system and leaves it after work interaction, which means that such processes occur in the systems having open boundary permitting mass interaction across the system boundary.