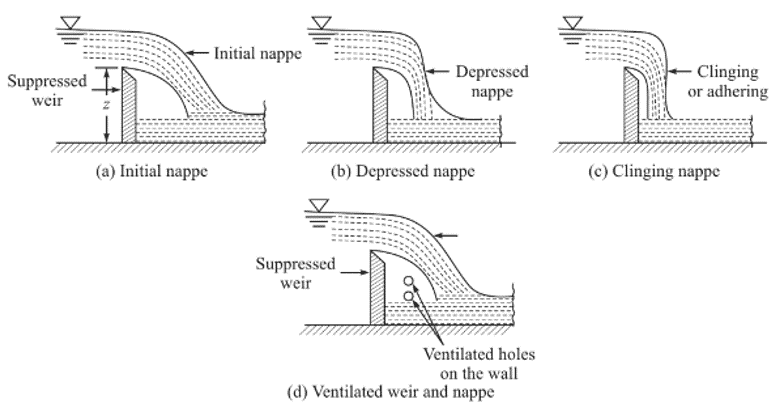
In hydraulic engineering, a nappe is a sheet or curtain of water that flows over a weir or dam. There are three types of nappe that form over the crest of a weir, depending on the air ventilation structure of a weir: free nappes, depressed nappes, and clinging nappes. A free nappe, which is ventilated to maintain atmospheric pressure below, does not come into contact with the underside of the weir. A depressed nappe is partially ventilated, which creates negative pressure beneath the nappe. In a depressed nappe the pressure below the nappe is negative.
3) In a depressed nappe
Answer is:
the pressure below the nappe is negative
Explanation:
Related Hydraulics and fluid mechanics MCQ with Answers
Answer is:
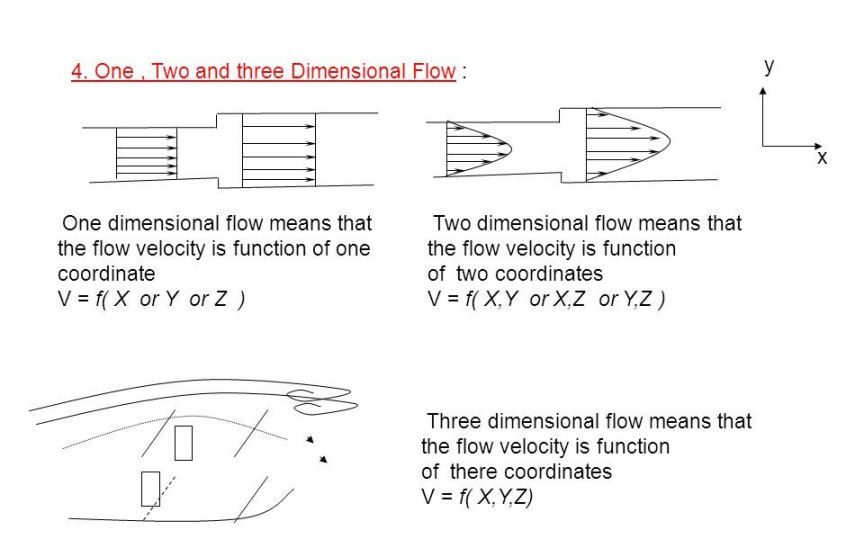
takes place in straight line
Explanation:
A flow, in which the streamlines of its moving particles are represented by a straight line, is called an one-dimensional flow.
Answer is:
ratio of absolute viscosity to the density of the liquid
Explanation:
Absolute viscosity or dynamic viscosity is defined as the property of a liquid which offers resistance to the movement of one layer of liquid over another adjacent layer of liquid. The viscosity of a liquid is due to cohesion and interaction between particles.
Kinematic viscosity is defined as the ratio of absolute viscosity to the density of the liquid.
Answer is:
more than
Explanation:
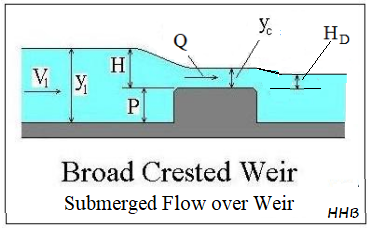
A weir is said to be broad crested weir, if the width of the crest of the weir is more than half the height of water above the weir crest.