When a liquid is contained in a vessel, it exerts force at all points on the sides and bottom of the vessel. The force per unit area is called intensity of pressure. Mathematically, intensity of pressure,
p = P/A
where
P = Force acting on the liquid, and
A = Area on which the force acts.
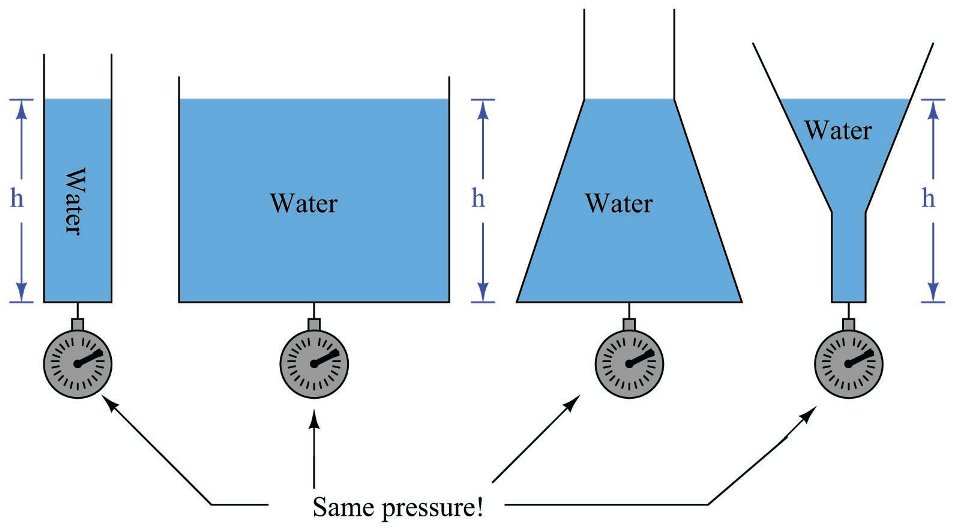
The intensity of pressure at any point, in a liquid at rest is equal to the product of weight density of the liquid (w) and the vertical height from the free surface of the liquid (h). Mathematically, intensity of pressure,
p = w. h
From this expression, we see that the intensity of pressure at any point, in a liquid, is directly proportional to depth of liquid from the surface.
114) The intensity of pressure on an immersed surface __________ with the increase in depth.
increases
Related Hydraulics and fluid mechanics MCQ with Answers
Agree
When a liquid is contained in a vessel, it exerts force at all points on the sides and bottom of the vessel. The force per unit area is called intensity of pressure. Mathematically, intensity of pressure,
p = P/A
where
P = Force acting on the liquid, and
A = Area on which the force acts.
The intensity of pressure may be expressed either in N/m2, N/mm2 or in metres of liquid or mm of liquid. Intensity of pressure is also expressed in pascal (briefly written as Pa), such that
1 Pa= 1 N/m2; 1 kPa= 1 kN/m2 and 1 MPa = 1 MN/m2= 1 N/mm2
According to Pascal’s law, the intensity of pressure at any point in a fluid at rest is same in all directions.
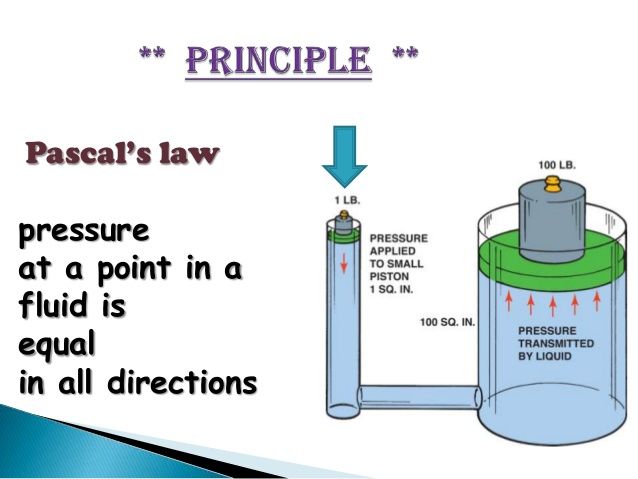
Correct
The important dimensionless numbers in fluid mechanics are
1. Reynold’s number
2. Froude’s number
3. Weber’s number
4. Euler’s number
5. Mach’s number or Cauchy’s number
Reynold’s number: Reynold’s number is the ratio of inertia force to the viscous force.
Froude’s number: Froude’s number is the ratio of inertia force to the gravity force.
Weber’s number: Weber’s number is the ratio of inertia force to the surface tension force.
Euler’s number: Euler’s number is the ratio of inertia force to the pressure force.
Mach’s number or Cauchy’s number: Mach’s number or Cauchy’s number is the ratio of inertia force to the elastic force.
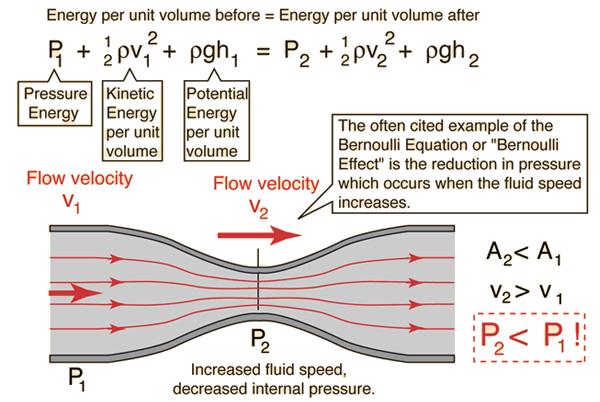
Bernoulli's equation
weight of the liquid displaced
When a body is immersed wholly or partially in a liquid, it is lifted up by a force equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the body. This statement is known as Archimedes principle.
The tendency of a liquid to uplift an immersed body, because of the upward thrust of the liquid, is known as buoyancy. The force tending to lift up the body is called the force of buoyancy or buoyant force and it is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced. The point through which the buoyant force is supposed to act, is known as centre of buoyancy. It may be noted that
1) If the force of buoyancy is more than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will float.
2) If the force of buoyancy is less than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will sink down.