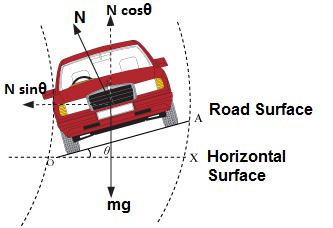
Whenever a roadway (or railway) is laid on a curved path, then its outer edge is always made higher than the inner edge, to keep the vehicle in equilibrium while in motion.
The amount by which the outer edge is raised, is known as cant or superelevation. In case of roadways, the process of providing superelevation is known as banking of the road.
The general practice, to define the superelevation in roadways, is to mention the angle of inclination (also called angle of banking) of the road surface.
In case of railways, the general practice to define the superelevation, is to mention the difference of levels between the two rails.
86) The slope on the road surface generally provided on the curves is known as
angle of banking
Related Engineering Mechanics MCQ with Answers
greater then
elastic bodies
Elastic bodies: The bodies which rebound after impact are called elastic bodies.
The impact between two rubber spheres is an elastic impact.
Inelastic bodies: The bodies which does not rebound at all after its impact are called inelastic bodies.
The impact between two lead spheres or two clay spheres is approximately an inelastic impact.
zero
Elastic bodies: The bodies which rebound after impact are called elastic bodies.
The impact between two rubber spheres is an elastic impact.
Inelastic bodies: The bodies which does not rebound at all after its impact are called inelastic bodies.
The impact between two lead spheres or two clay spheres is approximately an inelastic impact.
Coefficient of restitution is defined as the ratio of Relative velocity after impact to Relative velocity before impact. Coefficient of restitution is denoted by 'e'.
e = 0, For perfectly inelastic bodies .
e = 1, For perfectly elastic bodies.
0>e>1,(value of e lies between zero and one) For bodies neither perfectly inelastic nor perfectly elastic.