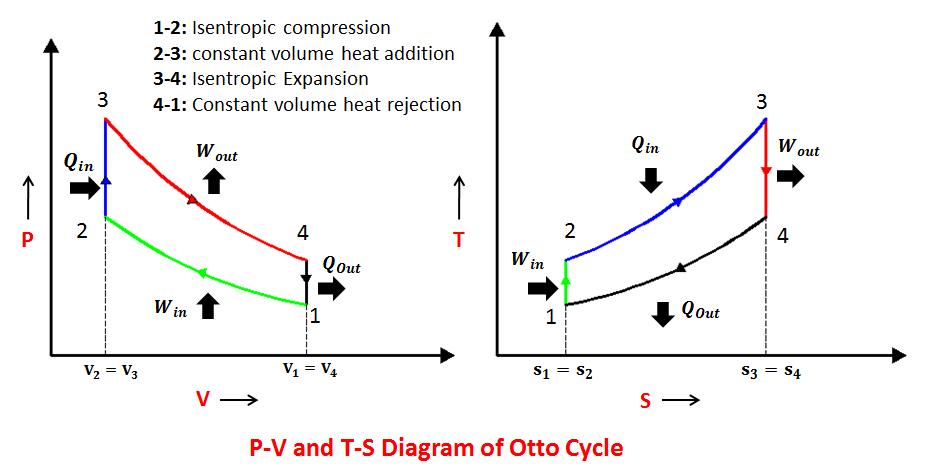
Otto cycle is also known as constant volume cycle, as the heat is received and rejected at a constant volume. Otto cycle is used in gas, petrol and many of the oil engines. The petrol engine works on Otto cycle.
The ideal Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two reversible adiabatic or isentropic processes.
Otto cycle is taken as a standard of comparison for internal combustion engines. For the purpose of comparison with other cycles, the air is assumed to be the working substance.
6) The petrol engine works on
Otto cycle
Related Automobile Engineering MCQ with Answers
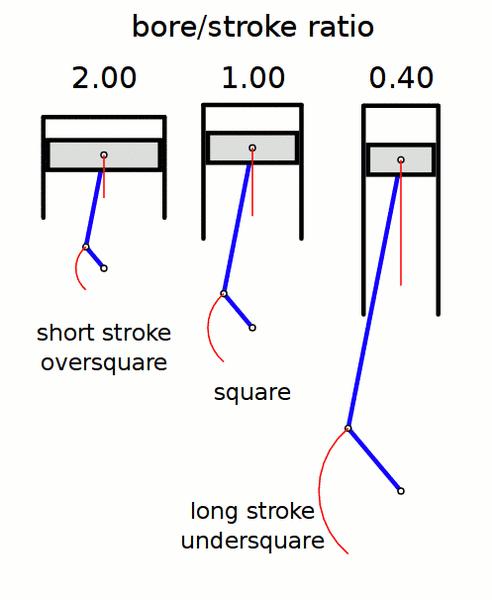
Stroke length and cylinder bore are same
A square engine is an engine with bore diameter equal to stroke length. D=L. An under-squared engine has stroke length greater than bore diameter (L >D). This means the engine generates more torque at low speeds. These can be found in heavy vehicles such as Harley Davidson.
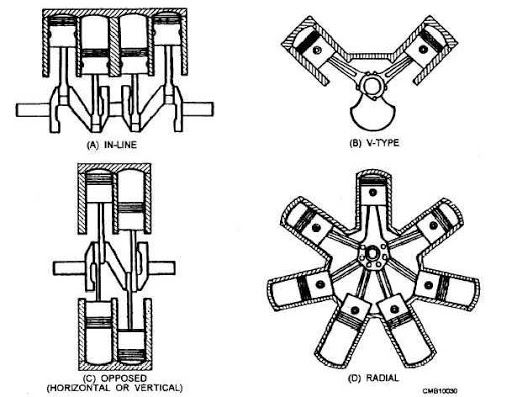
inline, V and opposed
In-line engine The cylinders are arranged in a single row, one behind the other. They may be vertical, as in most modern light vehicles, horizontal are used in coaches where the engine is positioned under the floor, or inclined at an angle to allow for a lower bonnet line.
Vee engine The cylinders are arranged in two rows at an angle to one another. The angle for two-, four- and eight-cylinder engines is usually 90 . For six- and twelve-cylinder engines the angle is usually 60.
Opposed piston or cylinder engine This is where the cylinders are at an angle of 180 apart and usually positioned horizontally
Spark ignition (S.I) engines
The most prominent difference between Spark Ignition (SI) and Compression Ignition (CI) engines is the type of fuel used in each. In SI engines petrol or gasoline is used as fuel, hence these engines are also called petrol engines. In CI engines diesel is used as fuel, hence they are also called diesel engines.

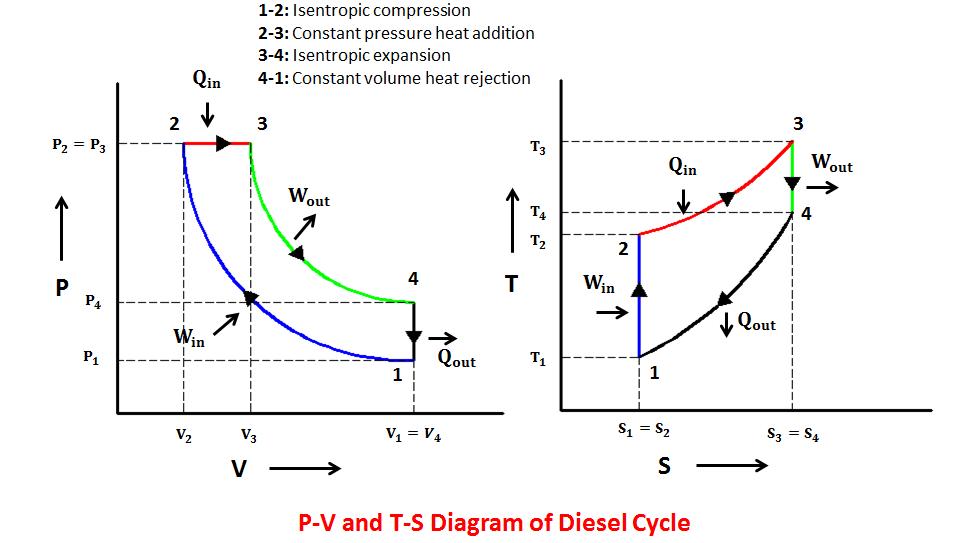
Diesel cycle
The Diesel cycle is a combustion process of a reciprocating internal combustion engine. In it, fuel is ignited by heat generated during the compression of air in the combustion chamber, into which fuel is then injected.
A Diesel cycle consists of one constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic processes.