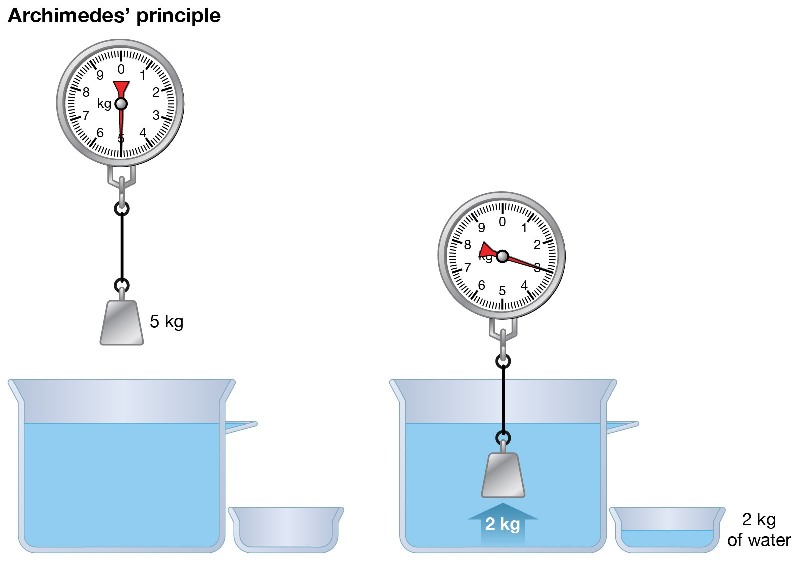
When a body is immersed wholly or partially in a liquid, it is lifted up by a force equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the body. This statement is known as Archimedes principle.
The tendency of a liquid to uplift an immersed body, because of the upward thrust of the liquid, is known as buoyancy. The force tending to lift up the body is called the force of buoyancy or buoyant force and it is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced. The point through which the buoyant force is supposed to act, is known as centre of buoyancy. It may be noted that
1) If the force of buoyancy is more than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will float.
2) If the force of buoyancy is less than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will sink down.
68) The resultant upward pressure of a fluid on a floating body is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. This definition is according to
Archimedes′ principle
Related Water Resources Engineering MCQ with Answers
buoyancy
When a body is immersed wholly or partially in a liquid, it is lifted up by a force equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the body. This statement is known as Archimedes principle.
The tendency of a liquid to uplift an immersed body, because of the upward thrust of the liquid, is known as buoyancy. The force tending to lift up the body is called the force of buoyancy or buoyant force and it is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced. The point through which the buoyant force is supposed to act, is known as centre of buoyancy. It may be noted that
1) If the force of buoyancy is more than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will float.
2) If the force of buoyancy is less than the weight of the liquid displaced, then the body will sink down.
all the above are correct
viscosity
Poise is the unit of dynamic viscosity. It is named after the French physicist Jean Louis Marie Poiseuille, who made important contributions to the study of fluid mechanics. The dynamic viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow when a force is applied to it. It is defined as the ratio of the shear stress to the shear rate of the fluid. The poise is a CGS (centimeter-gram-second) unit of dynamic viscosity, and it is equal to one dyne-second per square centimeter. Another commonly used unit of dynamic viscosity is the Pascal-second (Pa·s) in the SI (International System of Units) system. One poise is equal to 0.1 Pa·s.